Step into the realm of communication with the Purdue Model Diagram, a groundbreaking tool that illuminates the intricate stages of communication. Its multifaceted applications, from interpersonal relationships to corporate environments, make it an invaluable guide for fostering meaningful and effective interactions.
Delve into the diagram’s components, unraveling their interconnected functions and relationships. Witness the communication process unfold, stage by stage, as information flows through its channels. Explore the potential barriers that hinder effective communication and discover how to overcome them with the Purdue Model Diagram as your compass.
Overview of the Purdue Model Diagram
The Purdue Model Diagram is a graphical representation of the communication process, developed by Frank E. X. Dance and Carl E. Larson in 1976. It is a visual tool that helps users understand and analyze the different elements involved in communication, and how they interact with each other.
The Purdue Model Diagram has been widely used in various fields, including communication studies, education, and business. It has been particularly useful in helping people to understand the complexities of human communication, and to identify potential barriers to effective communication.
Components of the Purdue Model Diagram
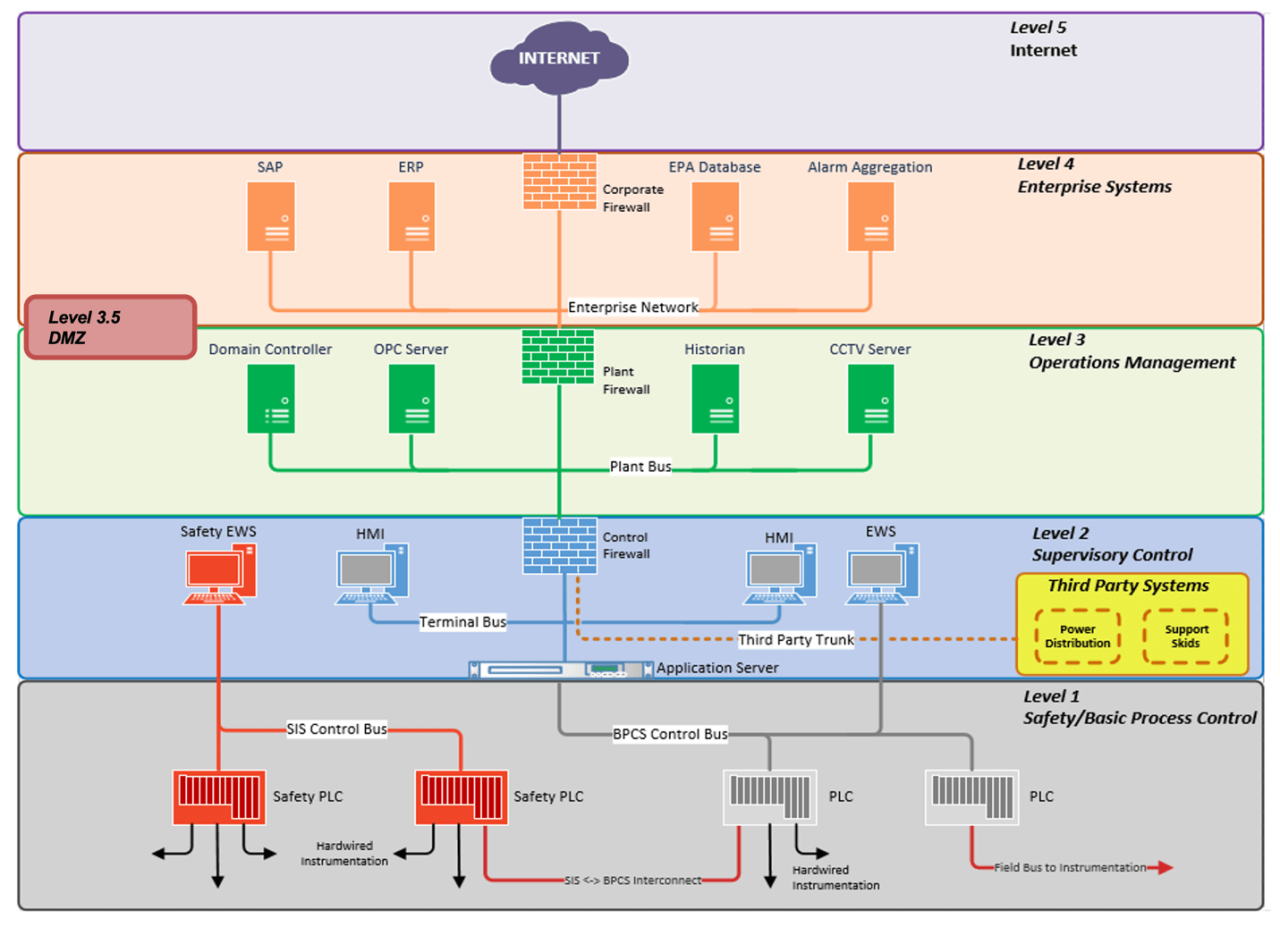
The Purdue Model Diagram is a visual representation of the communication process, which involves several key components that work together to facilitate effective communication. These components are:
- Source: The sender of the message, who initiates the communication process.
- Encoder: The component that converts the message into a form that can be transmitted.
- Channel: The medium through which the message is transmitted.
- Decoder: The component that interprets the received message.
- Receiver: The recipient of the message, who completes the communication process.
These components are interconnected and work in a sequential manner to ensure successful communication. The source generates the message, which is then encoded into a transmittable form by the encoder. The encoded message is sent through a channel to the receiver, where it is decoded and interpreted by the decoder. Finally, the decoded message is received by the receiver, completing the communication cycle.
Functions of Each Component
Each component of the Purdue Model Diagram has a specific function:
- Source: Generates and initiates the message.
- Encoder: Converts the message into a transmittable form, such as speech, writing, or electronic signals.
- Channel: Provides the medium for transmitting the message, such as airwaves, telephone lines, or computer networks.
- Decoder: Interprets the received message and converts it into a form that can be understood by the receiver.
- Receiver: Receives and comprehends the decoded message, completing the communication process.
These components work together to ensure that the message is accurately transmitted, interpreted, and received, enabling effective communication.
Stages of the Communication Process
The Purdue Model Diagram depicts communication as a sequential process involving multiple stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in the flow of information, and factors at each stage can significantly influence the effectiveness of the communication process.
Encoding
Encoding is the initial stage where the sender converts the message into a form that can be transmitted to the receiver. This involves selecting appropriate words, symbols, or gestures to convey the intended meaning.
Factors influencing encoding effectiveness include the sender’s knowledge, skills, and cultural background. Additionally, the sender’s emotions and biases can shape the way they encode the message.
Transmission
In the transmission stage, the encoded message is sent through a communication channel to the receiver. The channel can be verbal (e.g., face-to-face conversation, phone call), written (e.g., email, letter), or nonverbal (e.g., body language, gestures).
Factors affecting transmission effectiveness include the clarity of the message, the reliability of the channel, and the presence of noise or interference.
Decoding
Decoding is the process where the receiver interprets the transmitted message and assigns meaning to it. The receiver must understand the sender’s intended meaning by decoding the symbols, words, or gestures used.
Factors influencing decoding effectiveness include the receiver’s knowledge, skills, and cultural background. The receiver’s expectations and biases can also affect their interpretation of the message.
Feedback
Feedback is an essential component of communication that allows the receiver to provide a response to the sender. This response can indicate whether the message was received and understood, and it can also provide additional information or ask for clarification.
Factors influencing feedback effectiveness include the timeliness and clarity of the feedback, as well as the willingness of both the sender and receiver to engage in feedback.
Barriers to Effective Communication
Communication barriers are obstacles that prevent the successful exchange of information between individuals. They can arise from various factors, including language differences, cultural disparities, communication styles, and situational constraints.
Identifying and overcoming these barriers is crucial for effective communication. By understanding the potential roadblocks, communicators can proactively address them and enhance the clarity and efficiency of their interactions.
Types of Barriers
- Language Differences: When individuals do not share a common language, communication can become challenging. Language barriers can result in misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and communication breakdowns.
- Cultural Disparities: Cultural differences can influence communication styles, values, and expectations. Cultural barriers can arise when individuals from different cultural backgrounds have different ways of expressing themselves, interpreting messages, and understanding nonverbal cues.
- Communication Styles: Different communication styles can also hinder effective communication. Some individuals may be direct and assertive, while others may be indirect and avoidant. Mismatches in communication styles can lead to misunderstandings and conflict.
- Situational Constraints: External factors such as noise, time constraints, or physical distance can also act as barriers to effective communication. These constraints can make it difficult for individuals to hear, understand, or respond to messages.
Overcoming Barriers
Overcoming communication barriers requires a proactive approach. Communicators can employ various strategies to address these obstacles:
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon, slang, or technical terms that may not be understood by the receiver.
- Be Culturally Sensitive: Understand the cultural context of the communication and adapt your communication style accordingly.
- Match Communication Styles: Adjust your communication style to match the preferences of the receiver.
- Minimize Situational Constraints: Choose a communication channel that minimizes noise and distractions, and ensure sufficient time for effective communication.
Purdue Model Diagram Analysis
The Purdue Model Diagram can be a valuable tool for analyzing and addressing communication barriers. By breaking down the communication process into its component parts, the model helps identify potential barriers and develop strategies to overcome them.
The Purdue Model Diagram is a useful tool for understanding the relationship between different variables. It can be applied to a wide range of topics, including eclipse solar penumbra . By breaking down a complex topic into its component parts, the Purdue Model Diagram can help us to better understand the interactions between different factors.
This can be a valuable tool for decision-making and problem-solving.
For example, if a communication barrier is identified in the “Encoding” stage, the communicator can use the model to consider factors such as the clarity of the message, the choice of language, and the cultural context. By addressing these factors, the communicator can improve the effectiveness of their communication.
Applications of the Purdue Model Diagram
The Purdue Model Diagram is a valuable tool that can be applied in various settings to enhance communication effectiveness. Its versatility makes it adaptable to different contexts, facilitating improved communication within organizations, teams, and interpersonal relationships. Understanding the model’s applications can empower individuals to leverage its principles for successful communication outcomes.
In organizational settings, the Purdue Model Diagram provides a framework for structured communication. It enables organizations to establish clear communication channels, define roles and responsibilities, and streamline information flow. By identifying potential barriers and implementing strategies to overcome them, organizations can foster a culture of open and effective communication, leading to improved decision-making, enhanced collaboration, and increased productivity.
Teams, Purdue model diagram
Within teams, the Purdue Model Diagram promotes effective communication by facilitating shared understanding and reducing misunderstandings. It encourages team members to actively listen, provide constructive feedback, and engage in respectful dialogue. By incorporating the model’s principles into team communication practices, teams can improve their ability to collaborate, solve problems, and achieve their goals.
Interpersonal Relationships
In interpersonal relationships, the Purdue Model Diagram can enhance communication by fostering empathy and understanding. It encourages individuals to consider different perspectives, actively listen to each other, and communicate their thoughts and feelings in a clear and respectful manner. By applying the model’s principles, individuals can build stronger relationships, resolve conflicts effectively, and create a more harmonious and fulfilling interpersonal environment.
Diverse Cultural Contexts
The Purdue Model Diagram is adaptable to diverse cultural contexts. It provides a common framework for communication, regardless of cultural differences. By understanding the cultural nuances and communication styles of different groups, individuals can tailor their communication approach to be more effective. The model promotes cultural sensitivity, encourages open dialogue, and fosters mutual respect, enabling effective communication across cultural boundaries.
Final Thoughts
As we bid farewell to this exploration, remember the Purdue Model Diagram as a beacon of communication clarity. Its versatility empowers us to navigate diverse cultural contexts and bridge interpersonal divides. Embrace its principles to elevate your communication skills, fostering deeper connections and unlocking the true potential of human interaction.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of the Purdue Model Diagram?
The Purdue Model Diagram provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the communication process, enabling us to analyze and improve communication strategies.
How can I use the Purdue Model Diagram to enhance my communication skills?
By studying the components and stages of the Purdue Model Diagram, you can identify areas for improvement and develop techniques to overcome communication barriers.
Can the Purdue Model Diagram be applied to different cultural contexts?
Yes, the Purdue Model Diagram is adaptable to diverse cultural contexts, offering insights into the unique communication styles and norms of different cultures.